As organizations shift toward multi-cloud environments and real-time service delivery, edge computing is becoming central to modern application strategies. But this decentralization introduces new security challenges. With devices and data distributed across multiple locations, securing the edge is no longer optional.
What does edge security really mean?: It’s about protecting applications, data, and services that are processed and delivered outside traditional data centers—closer to users and devices. This requires securing each edge node against attacks, ensuring encrypted communication, and maintaining control over who and what accesses your infrastructure, even in highly distributed environments.
Modern Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs)—like SKUDONET—play a key role in building resilient and secure edge infrastructures.
What Is Edge Computing and Why It Matters
Edge computing is a distributed IT architecture where data processing takes place as close as possible to the data source—rather than relying exclusively on centralized cloud infrastructures.
This approach addresses critical needs in modern application delivery: real-time responsiveness, reduced latency, and local autonomy. By processing data at the edge of the network, organizations minimize the delay associated with long-distance data transmission and ensure better service continuity, even in scenarios where connectivity is limited or intermittent.
Key benefits of edge computing for secure and efficient application delivery:
- Reduced latency: Critical in use cases that demand real-time data processing.
- Optimized bandwidth: Only relevant data is transmitted to the cloud or data center.
- Improved reliability: Applications can continue functioning even when the connection to the core network is disrupted.
- Enhanced scalability: Distributes workloads more efficiently across edge and core environments.
Edge computing plays a fundamental role in modern IT strategies, particularly when combined with security, observability, and automation—areas where SKUDONET provides integrated support for robust application delivery.
Common Edge Security Threats
As edge infrastructure grows, so does its exposure to security risks. The combination of distributed endpoints, increased network complexity, and reliance on real-time connectivity makes the edge a prime target.
Key threats include:
- DDoS attacks targeting edge nodes to degrade or halt local services.
- Malware and ransomware infiltrating through unmanaged or poorly secured devices.
- Compromised or unmonitored IoT devices can serve as entry points for broader network intrusions.
- Data interception over insecure communication channels.
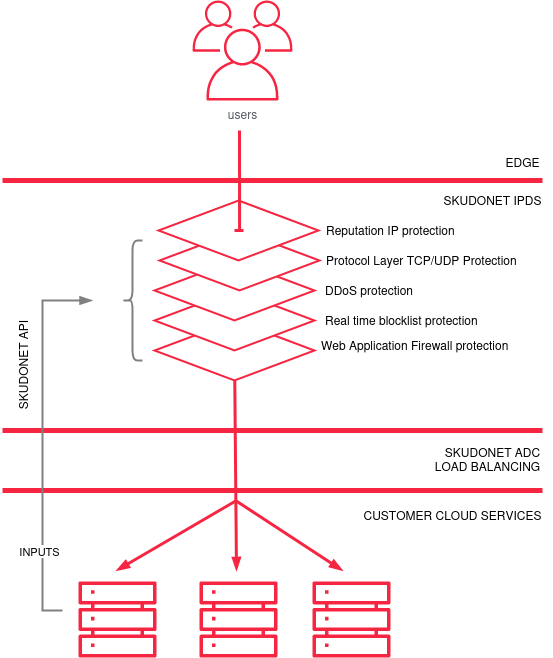
Securing the Edge with SKUDONET
SKUDONET Enterprise Edition provides an integrated ADC and load balancing solution built with security at its core—critical in edge environments.
Key features for edge security:
Secure Application Load Balancing
SKUDONET ensures that traffic distribution across nodes is not only efficient, but also resilient against malicious traffic patterns. Rate limiting, health checks, and session persistence features protect against overload and improve reliability.
Built-in Web Application Firewall (WAF)
The Enterprise Edition of SKUDONET includes an advanced WAF as a core feature, providing application-layer protection without requiring external modules. It mitigates common threats such as SQL injection, XSS, and OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities.
DDoS Protection and Traffic Filtering
Advanced filtering mechanisms allow for early detection and blocking of suspicious traffic. When deployed at the edge, this helps stop attacks before they propagate deeper into the network. The SKUDONET IPDS module operates at the edge, providing a layered defense that includes IP reputation filtering, protocol-level protection, DDoS mitigation, real-time blocklists, and Web Application Firewall—all before traffic reaches the load balancing tier.
SSL/TLS Termination and Encryption
SKUDONET supports SSL offloading and re-encryption, ensuring data confidentiality across all connections. This reduces the load on backend services and improves response times.
Access Control and Authentication
Role-based access, IP whitelisting, and integration with identity providers support granular control over who accesses edge applications.
Edge computing is no longer a future trend—it’s a current reality. As organizations distribute their infrastructure to improve performance and user experience, edge security becomes a non-negotiable requirement.
SKUDONET enables secure application delivery at the edge by combining advanced load balancing with integrated threat protection, all managed from a centralized interface.
Discover SKUDONET Enterprise Edition or Try it for free for 30 days.