When a company evaluates an Application Delivery Controller, one of the key questions that often comes up is: Does it allow for traffic inspection?
But this question is more complex than it seems. Traffic inspection is a critical capability in many Application Delivery Controllers (ADCs), but its meaning can vary depending on the context, the depth of analysis, and the expected functionalities.
In this article, we explain what traffic inspection actually means in an ADC, why it matters, and what capabilities SKUDONET offers in this area.
Not All Inspection Is the Same
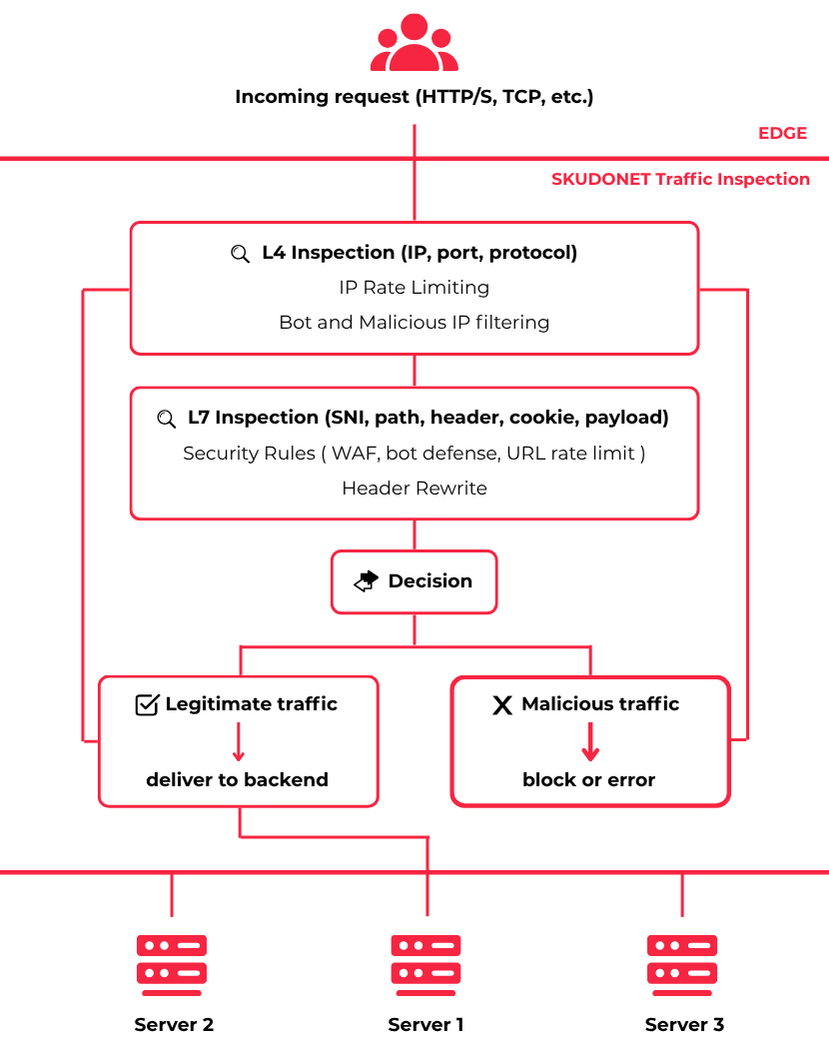
When an ADC inspects traffic, it can do so at different layers of the OSI model and with different purposes. The most common types include:
Layer 4 (L4) Inspection
At this level, the ADC analyzes network connections (TCP/UDP). It examines basic headers such as IP addresses, ports, and protocol type. This enables fast and efficient load balancing without needing to parse the content of the request.
- Advantages: Very high performance, minimal latency
- Limitations: No visibility into the request content
Layer 7 (L7) Inspection
Here, the ADC analyzes the actual content of the request at the application layer (HTTP, HTTPS, etc.). It can inspect HTTP headers, paths, cookies, URL parameters, or even the payload.
- Advantages: Enables smarter decisions based on real content
- Limitations: Requires more processing power; may affect performance if not optimized
Why Is Traffic Inspection Useful?
Traffic inspection capabilities in an ADC enable logic-based decisions according to the content and behavior of the traffic:
- Content-based routing (content switching): Direct traffic based on headers, paths, or cookies.
- Filtering and control: Block specific patterns, handle exceptions, or restrict access based on custom criteria.
- Security: Detect suspicious traffic, block dangerous requests, and protect against application-level threats like SQL injection or XSS.
- Response optimization: Adapt behavior depending on the client type, browser, or geographic location.
Additionally, in environments where proxies or other intermediaries are used, ADCs can detect and mitigate header spoofing (e.g., X-Forwarded-For), which is crucial when tracing the actual origin of a request.
What Traffic Inspection Capabilities Does SKUDONET Offer?
SKUDONET ADC provides a flexible traffic inspection system with a wide range of capabilities to adapt to various environments:
- Bot and malicious traffic filtering at Layer 4 for high-speed preemptive protection, enabling early blocking of suspicious connections before deeper inspection is needed.
- Header, cookie, and HTTP parameter inspection for routing, filtering, or blocking decisions at Layer 7.
- API rate limiting based on URL patterns, request methods, or IP behavior — essential for protecting exposed endpoints.
- Header rewriting and modification based on defined rules.
- Custom responses for specific conditions, such as blocking suspicious or malformed requests.
- Advanced certificate management, including wildcard support and granular SNI-based configuration.
- Access control logic based on origin, methods, paths, or geolocation.
- Intuitive graphical interface to define rules easily — or direct config access for manual or automated setups.
These features enable deep control of HTTP/HTTPS traffic while combining speed and visibility — adaptable to both simple environments and complex architectures.
Traffic inspection in an ADC isn’t just about watching the data stream — it’s about understanding it and responding accordingly. The ability to inspect headers, analyze content, and take intelligent, real-time actions is what sets advanced solutions apart from limited ones.
SKUDONET Enterprise Edition enables efficient Layer 7 traffic inspection, offering detailed rules, deep visibility, and flexible configuration — all with a transparent, architecture-agnostic approach.